Water is often referred to as the universal solvent, but its role in chemistry goes far beyond merely dissolving substances. Take a closer look at Hcooch Ch2 H2o, for instance. This intriguing compound showcases how water can stabilize and influence chemical structures.
Imagine water acting like a supportive friend, helping compounds maintain their integrity during reactions. It’s not just an essential ingredient; it plays a critical part in shaping molecular interactions and stability. As we dive into the fascinating interplay between Hcooch Ch2 H2o and water, you’ll discover why understanding this relationship is pivotal in both scientific research and industrial applications. Let’s explore how water’s unique properties contribute to the stability of various compounds!
The Importance of Water in Chemical Reactions
Water is often dubbed the universal solvent, and for good reason. Its unique properties enable it to facilitate countless chemical reactions. As a polar molecule, water can interact with various substances, breaking them apart or allowing them to combine in new ways.
In biochemical processes, water acts as both a reactant and a product. For example, in hydrolysis reactions, it cleaves larger molecules into smaller units by adding itself into the mix. This reaction is crucial for digestion and energy production in living organisms.
Moreover, temperature regulation plays an essential role in these reactions. Water’s high specific heat capacity allows systems to maintain stable temperatures during exothermic or endothermic changes. This stability fosters optimal conditions for complex molecular interactions.
Without water’s mediating presence, many vital chemical processes would not occur efficiently or at all. It truly is indispensable across various scientific domains.
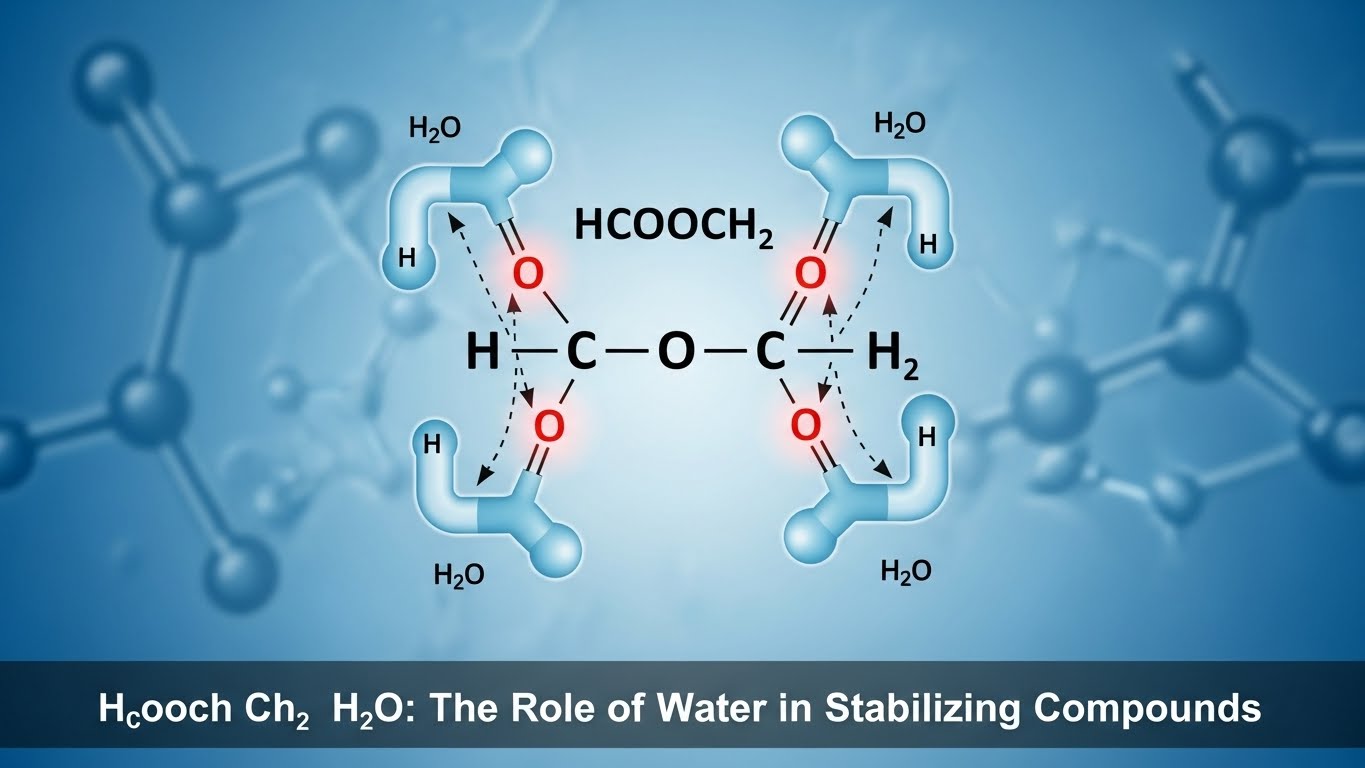
Water’s Role in Stabilizing Compounds
Water acts as a crucial stabilizing agent in chemical reactions. Its unique molecular structure enables it to interact effectively with various compounds.
When Hcooch Ch2 H2o is present, water molecules form hydrogen bonds that help maintain the integrity of the compound’s structure. These interactions create a more stable environment for chemical processes.
Moreover, water can influence solubility and reactivity. By dissolving substances, it facilitates easier access for reactants to collide and react.
In many cases, the presence of water reduces energy barriers during reactions. This lower activation energy fosters stability within compounds like Hcooch Ch2 H2o.
Additionally, water’s polarity allows it to stabilize charged species by surrounding them with solvent molecules. This characteristic ensures that sensitive compounds remain intact under varying conditions.
Understanding these dynamics opens new avenues for research and application in chemistry.
Case Study: The Stability of Hcooch Ch2 H2o compared to other compounds
The stability of Hcooch Ch2 H2o presents an intriguing case when compared to other chemical compounds. Its unique structure allows for efficient interactions with water molecules, enhancing its integrity.
For instance, when examined alongside simple alcohols or carboxylic acids, Hcooch Ch2 H2o demonstrates superior resilience under varying temperatures and pressures. The hydrogen bonding capabilities play a pivotal role in maintaining its structural strength.
Moreover, this compound’s ability to remain stable during reactions highlights the effectiveness of water as a stabilizing agent. Unlike more volatile substances that succumb to rapid degradation, Hcooch Ch2 H2o retains its form longer.
This characteristic not only informs scientists but also serves practical applications across industries such as pharmaceuticals and agriculture. Understanding these differences can lead to innovative solutions and improved formulations in various sectors.
Factors Affecting Water’s Stabilization Abilities
Several factors influence water’s stabilization abilities in chemical compounds. Temperature plays a crucial role. As temperature increases, molecular motion heightens, potentially reducing the effectiveness of water as a stabilizing agent.
pH levels are another significant factor. Acidic or alkaline environments can alter the interactions between water molecules and solutes. This shift can either enhance or diminish stability depending on the specific chemical makeup of the compound involved.
The presence of salts and other solutes also impacts how well water stabilizes compounds. Ionic strength changes the dynamics within aqueous solutions, often leading to increased or decreased solvation effects.
Hydrogen bonding is vital for stabilization. The orientation and strength of these bonds significantly affect how well compounds like Hcooch Ch2 H2o maintain their structure in various conditions. Understanding these intricacies helps chemists predict behaviors in different scenarios effectively.
Applications of Water Stabilization in Industries
Water stabilization finds wide applications across various industries, enhancing both safety and efficiency. In pharmaceuticals, water plays a critical role in maintaining the stability of active compounds in drug formulations. This ensures that medications remain potent and effective over time.
In agriculture, it helps stabilize nutrients within fertilizers. The presence of water enables better absorption by plants, promoting healthier growth and higher yields.
The food industry also benefits significantly from this phenomenon. Water stabilizes emulsions and suspensions in products like sauces or dressings, ensuring consistent texture and taste.
Moreover, industrial processes such as chemical manufacturing rely on water to maintain stable reaction conditions. Controlled environments prevent unwanted reactions that could compromise product quality or safety.
Even in construction materials like concrete, proper moisture levels help achieve optimal strength and durability. These diverse applications underscore the essential role of water stabilization across sectors.
The Significance of Understanding Water’s Role in Chemistry
Understanding water’s role in chemistry is crucial for multiple scientific disciplines. Water is often referred to as the universal solvent, playing a significant part in various chemical reactions.
Its unique properties allow it to stabilize compounds like Hcooch Ch2 H2o, impacting everything from drug formulation to agricultural practices. By grasping how water interacts with different substances, chemists can predict reaction outcomes more accurately.
Furthermore, comprehending these interactions aids researchers in developing innovative solutions for environmental challenges.
Knowledge of water’s stabilizing effects also enhances our understanding of biological systems where hydration levels directly influence metabolic processes.
In every sector that relies on chemistry, the significance of water cannot be overstated. It serves as both a reactant and a medium essential for countless applications across industries.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of water in stabilizing compounds like Hcooch Ch2 H2o is crucial for many scientific disciplines. Water acts as a versatile solvent, influencing chemical reactions and compound stability. The unique properties of water allow it to interact with different molecules, enhancing their stability.
The case study comparing Hcooch Ch2 H2o with other compounds highlights how water can make a significant difference. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration also play essential roles in determining how effectively water can stabilize various substances.
Industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to agriculture benefit immensely from these insights. Applications include drug formulation and agricultural practices that rely on stable compounds for optimal results.
A deeper understanding of how water interacts with chemistry not only enhances our knowledge but paves the way for innovations across multiple fields. As research continues to unfold, the implications of these interactions will likely lead to new discoveries that further accentuate the significance of this simple yet powerful molecule.