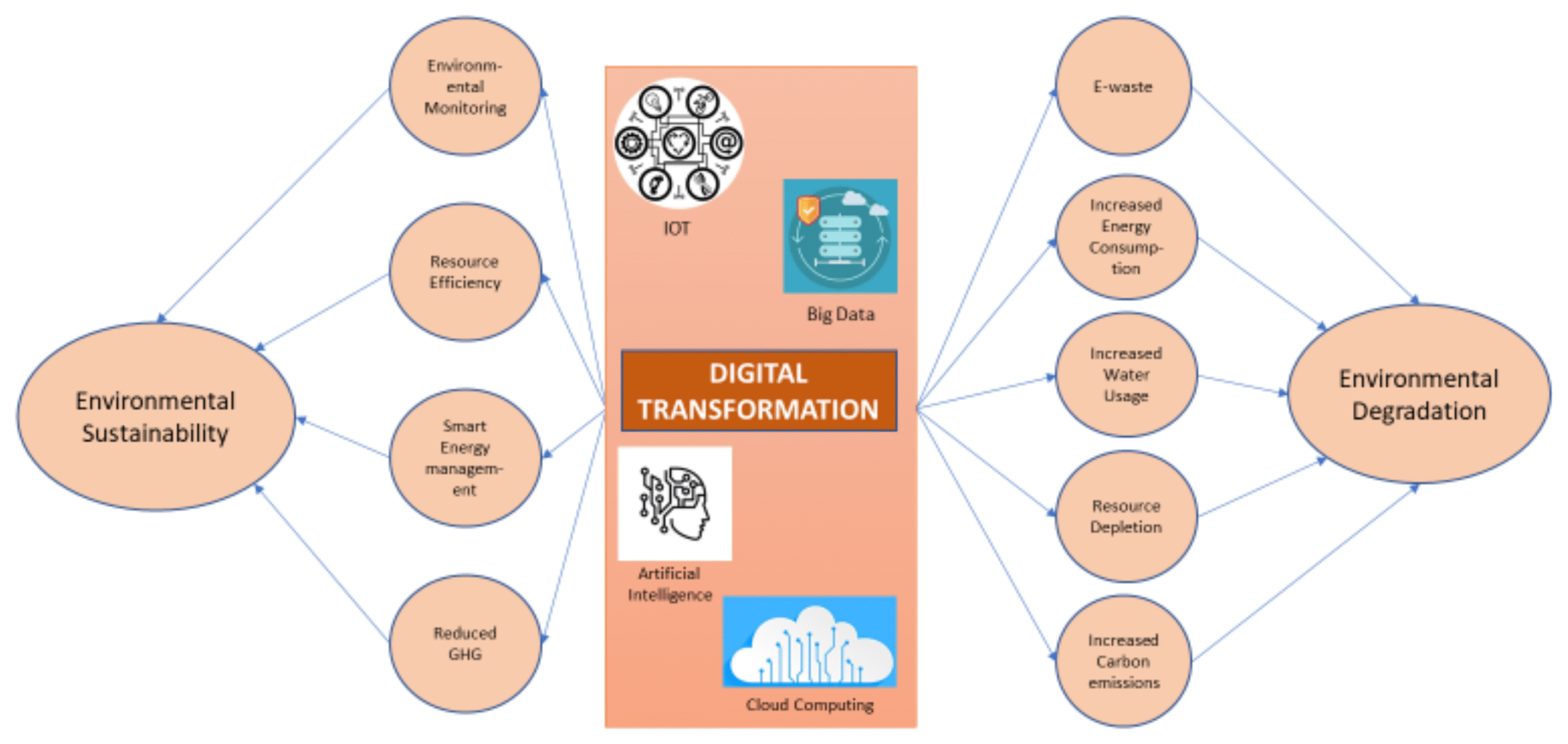
As more of our lives move online, the environmental cost of our digital habits is becoming harder to ignore. From streaming high-definition videos to backing up endless gigabytes of photos, digital storage consumes real-world resources often with a carbon footprint that goes unnoticed.
While the cloud might feel intangible, it’s supported by vast physical infrastructure. Data centers housing millions of servers run around the clock, using enormous amounts of electricity for both computing and cooling. As demand for data grows, so too does the environmental burden.
One contributing factor is the inefficiency of storing unoptimized media. For example, converting videos from AVI to MP4 reduces file sizes without sacrificing quality saving space and energy across storage and streaming platforms. Simple steps like this can significantly cut down on digital waste.
How Data Storage Impacts the Environment
Most people don’t think twice about uploading another photo or downloading another file, but each digital action requires energy. The data you save online is stored in a facility that needs:
- Electricity to power servers
- Cooling systems to prevent overheating
- Backup power and security systems
According to estimates, data centers account for around 1-1.5% of global electricity use. That may not seem like much, but as digital consumption increases exponentially, so does the associated energy demand.
The Hidden Cost of Streaming
Streaming is one of the biggest contributors to digital energy use. Watching a 4K video on a platform like YouTube or Netflix requires more bandwidth and processing power than lower-resolution formats. When billions of people stream daily, the combined effect becomes significant.
The carbon footprint of streaming an hour of HD video is comparable to boiling a kettle multiple times. Multiply that by hours per day, per person and the impact adds up.
How File Optimization Reduces Digital Waste
One way to reduce the environmental footprint of digital storage is by optimizing files. Smaller files use less space and require less bandwidth to transmit. This is particularly true for video, which tends to be data-heavy.
Converting files from large, outdated formats (like AVI) to modern, compressed ones (like MP4) helps reduce size without compromising quality. Using tools to convert AVI to MP4 is a simple, effective way to lessen the environmental impact of storing and sharing media.
Data Hoarding: A Growing Concern
We’re storing more data than ever often unnecessarily. Duplicate photos, outdated backups, and old downloads clutter personal devices and cloud services alike. While it may not seem like a big deal, collectively, this habit drives demand for more storage infrastructure.
Regularly deleting unneeded files, optimizing media, and being mindful about uploads can help limit digital clutter and the energy it consumes.
Solutions and Industry Efforts
The good news: awareness of the environmental cost of data is growing, and many companies are taking steps to reduce their impact. Some notable efforts include:
- Green data centers: Facilities powered by renewable energy sources.
- Efficient cooling systems: Liquid cooling and outside-air ventilation reduce energy use.
- Data compression and deduplication: Reducing redundant data minimizes storage needs.
Tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Apple are investing in sustainability goals for their cloud services. But user behavior also plays a role especially when it comes to the size and quantity of data stored.
What You Can Do
Here are a few easy steps you can take to reduce your digital carbon footprint:
- Delete files you no longer need
- Compress photos and videos before uploading
- Stream in lower resolution when possible
- Use cloud storage services with green certifications
- Convert large video files to efficient formats like MP4
Making environmentally conscious decisions with your digital habits helps reduce the strain on infrastructure and ultimately, the planet.